IT Blog: Phishing
Welcome to the third IT blog which this week concentrates on Phishing. I chose this topic to follow on from passwords as this technique is a commonly used approach from cyber attackers to get access to your credentials and then possibly your online identity.
Phishing is a cleverly put together word that describes what an attacker does, they send out a hook and hope that someone bites. Very similar to the popular hobby of fishing but without the need to be freezing halfway out in a lake and coming home smelling of fish.

So how do they do they do it. In most cases they will send out an email to hundreds sometimes thousands of people taking advantage of either current events (Covid, Christmas sales, Fuel rises, Tax year), personal accounts (Banking, Streaming services, social media, Shopping) or corporate process (HR, Finance, IT). They commonly use available names from website or social media and company logos to make it look more realistic and believable.
Key things to look out for in a phishing email are
- Incorrect email addresses.
- Spelling mistakes.
- Language used if it is from a corporate account is it professional?
- Tone, do they usually communicate in this way?
- Links, if you hover over a link, it will tell you where it is going. This should usually reflect the company that has sent it.
- Layout, like language does it look official.
Spending the extra time to review all these points can save you a whole lot of pain. If you are not sure at any point you need to either investigate further if you think it is legitimate or just ignore and delete.
To help you see what these could look like I have added two examples that could be from college accounts. To be clear they aren’t but you can see how easy it is to fall for them.
Example 1
The first example we explore has a context (Covid) with a serious background that already builds up your confidence that it is legitimate.
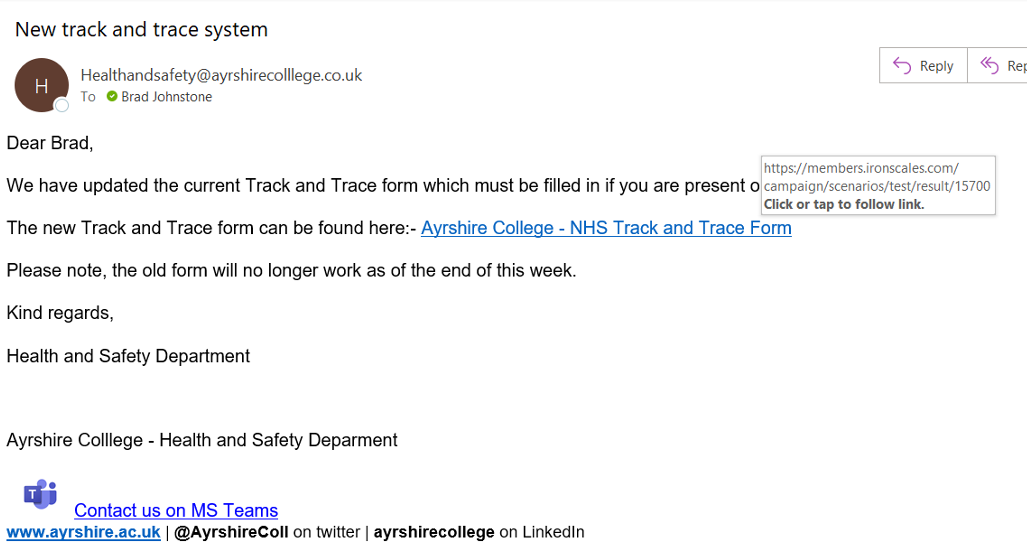

So what are the signs that this is a phishing email?
The first is the email address, not only is it one that the college doesn’t use it is also misspelt with 3 ‘L’ in it.
The second is the white box which is there because I hovered over (not clicked) the link in the email. This provides the where the link goes, this should be related to the college in some way.
The third which might not be as obvious is the term ‘Track and Trace’ which is the term England used. Scotland used the term ‘Test and Protect’.
Example 2
The second example we explore is an offer that seems too good to be true.
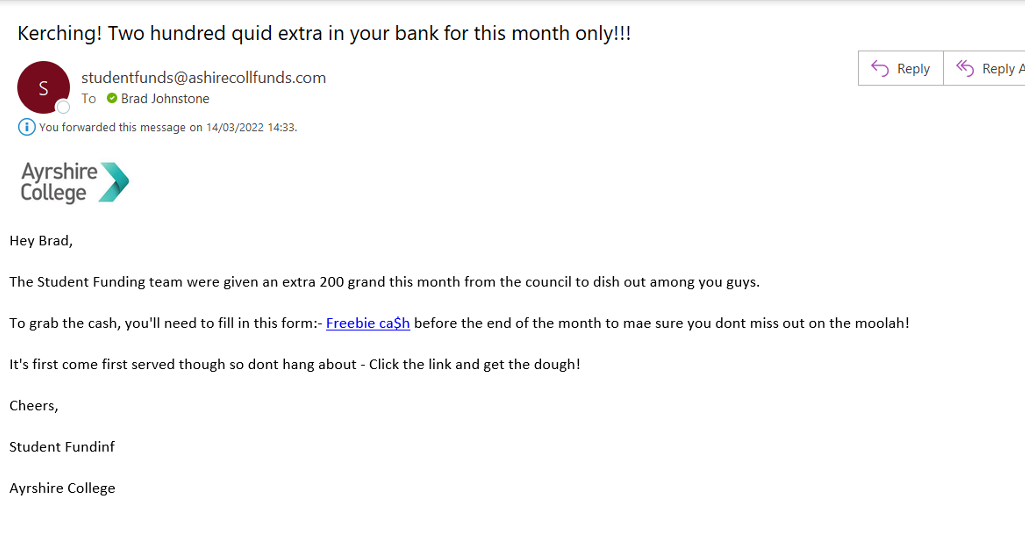

So what are the signs that this is a phishing email ?
The first and main sign that this isn’t legitimate is that is written in a highly unprofessional manner. Our student funding team along with all our teams wouldn’t send out an email or any communication using this type of language. Examples are Kerching, quid, 200 grand, moolah and dough. This is a key difference to example 1 where it is worded in a professional manner.
The second is the email address, again this isn’t one that the college uses.
What can you do?
If you are unsure if the email is legitimate the best advice, I can give is to contact the sender or organisation to ask them. DO NOT reply to the email to ask them as they will engage in the communication and work to make you believe them. In these instances, I would advise you search for the company’s website (college in these examples) and find a contact number. This isn’t fool proof as there has been instances where hackers can create sites just for this purpose, so you still need to be cautious.
If you find that you have clicked on a link or shared details by falling victim to Phishing the first thing to do is change your password in any site that you use the username and password that you entered when clicking on the site. If you never got asked for your details, you may have indirectly installed malware on your device and you need to run a virus/malware checker.
Finally try not to panic or feel embarrassed these scams are becoming more and more sophisticated.
Next Week
Next week I will be discussing password managers and multi-factor authentication which are two ways to help protect and limit the impact if you lose your credentials through Phishing.
_____________________________________________________________________
Read Next
Click here to read our Password Managers and Multifactor Authentication blog next